Executive Summary
- Neo_Net’s Cybercrime Syndicate
This blog post provides insights into Neo_Net, a major player in the Spanish eCrime ecosystem from 2021 to 2023. Neo_Net targets clients of European financial institutions and offers services to facilitate cybercriminal activities.
- Evolution of Techniques
Neo_Net continually improves his methods, reusing tools and building a network of affiliates who rent them. He adapts to different scams and refines his approach over time.
- Targeted Financial Institutions
Neo_Net focuses on Spanish financial institutions, using advanced phishing panels to trick victims into revealing banking credentials. He employs tactics to avoid detection, such as geofencing, mobile traffic restrictions, and anti-scraping measures. Moreover, his OTP bots have been observed targeting German, French, Austrian, British, Dutch, Polish and Greek banks.
- Smishing-as-a-Service
Ankarex, Neo_Net’s Smishing-as-a-Service platform, remains active and evolving. It delivers fraudulent SMS messages, with ongoing enhancements including new routes and improved infrastructure
- Affiliates and Future Threats
Neo_Net collaborates with a network of affiliates, primarily Spanish-speaking, who target various financial institutions. This network highlights Neo_Net’s effectiveness and the potential risks he poses. Future plans include expanding the Smishing service and introducing new offerings for sophisticated scams.
Introduction
Neo_Net, a prominent actor within the Spanish eCrime ecosystem, has been active from mid-2021 until April 2023, primarily targeting clients of major European financial institutions. His operations involve the development of service offerings and assistance to other cybercriminals in setting up sophisticated scams. These include a Smishing-as-a-Service platform, OTP bots, and phishing panels. Throughout his career, Neo_Net has continually refined his techniques by reusing and iterating upon previously employed tools, while also establishing a network of affiliates who rent and utilize these tools for their own campaigns. This blog post provides an in-depth analysis of Neo_Net’s evolution over the years, highlighting key operational details and persistent patterns observed.
Humble Beginnings
The earliest observed malicious activity attributed to Neo_Net dates back to August 2021, when the threat actor initiated a crypto wallet phishing scheme utilizing Google Ads as the initial infection vector.
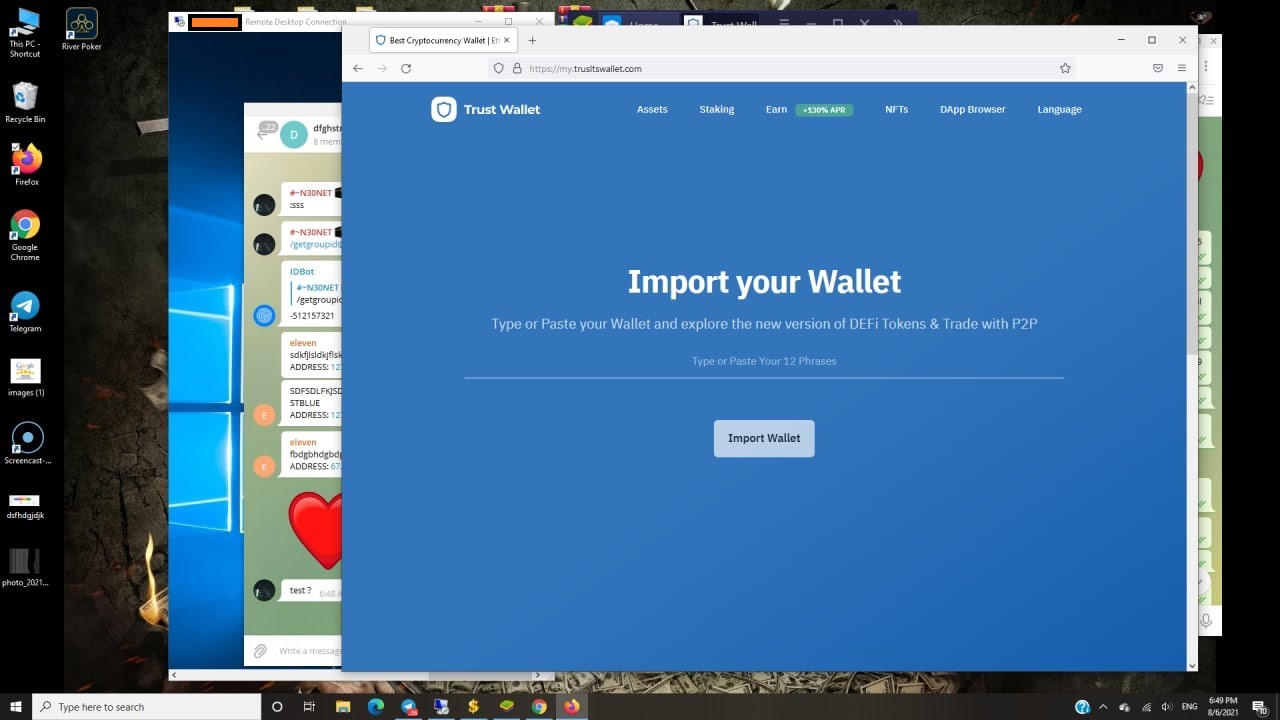
Figure 1: Fake crypto wallet phishing site
This scheme was conducted in collaboration with an individual known by the Telegram handle “devilteam666.” Neo_Net had already started leveraging Telegram channels to extract credentials, specifically seed phrases, a tactic that would later become a fundamental aspect of his operations.
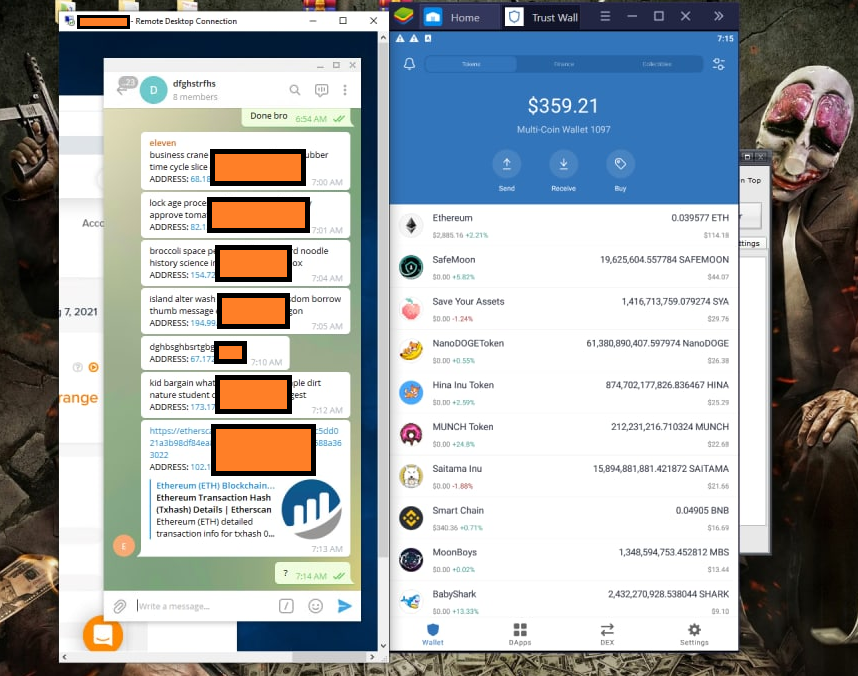
Figure 2: Exfiltrated seed phrases Telegram chat and hacked wallet
In addition to stealing seed phrases, the malicious page logged the victim’s IP address. This scam operated for at least a month, from 25 July to 16 August 2021. Based on conversations among the criminals in the Telegram chat, it generated a minimum profit of $20,000 USD during that period. The targeted wallets included Trust Wallet, Exodus Wallet, and MetaMask.
Targeting Financial Institutions
Neo_Net began targeting Spanish financial institutions as early as December 2021, utilizing specially designed phishing panels. These panels demonstrated advanced functionality, providing multiple user access and finely tuned settings to deceive victims into revealing their banking credentials.
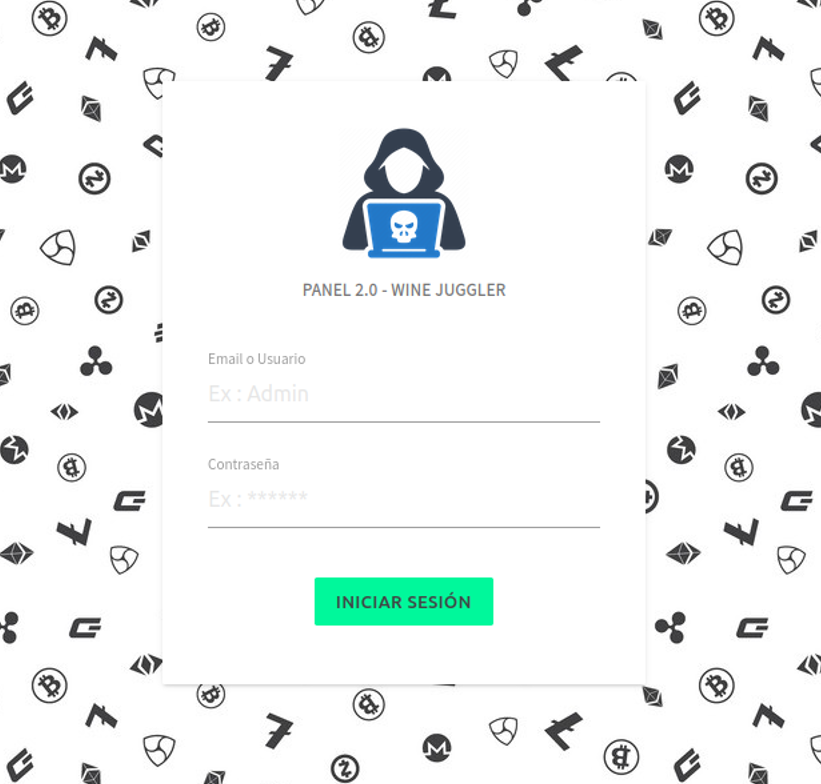
Figure 3: Wine Juggler Panel login page
To evade detection by security researchers or web scrapers, the panels featured settings that enabled geofencing to restrict access to a specific country, allowed only mobile traffic, and prevented popular scrapers from identifying the page. Victims who landed on the phishing site through malicious links were presented with fake landing pages impersonating various financial institutions.
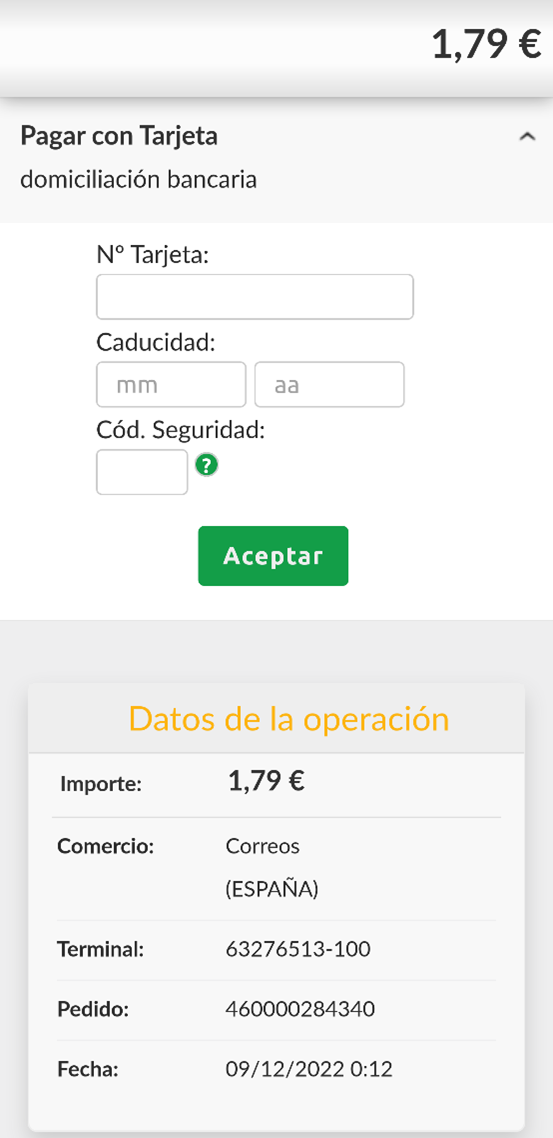
Figure 4: Phishing page impersonating Correos
Upon the victim’s entry of credentials, the panel accessed its configuration to retrieve the Telegram Bot ID, chat ID, and a redirect URL for visitors from non-preferred countries. These settings were then used to forward the credentials to the operators.

Figure 5: Configuration for a phishing panel targeting Abanca
Furthermore, the panel incorporated functionality that automatically prompted the victim to provide a single One-Time Password (OTP) to complete the login process with the provided credentials. However, this approach proved limited when additional transactions required additional OTPs, prompting Neo_Net to employ Android trojans capable of exfiltrating every incoming SMS message, facilitating the capture of subsequent OTPs.
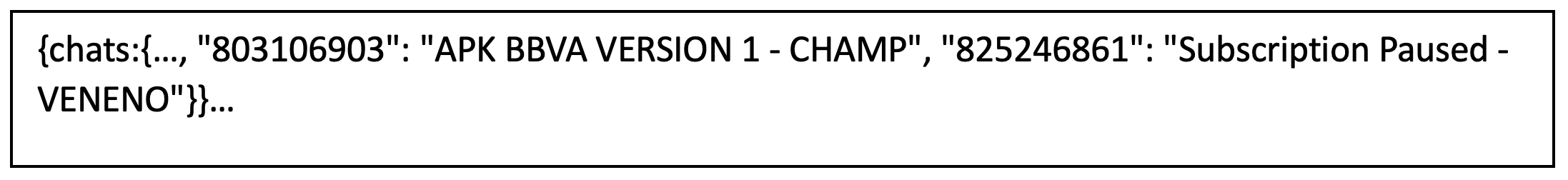
Figure 6: Telegram chat names for one of the OTP bots
Some of the chat names used in Neo_Net’s latest campaign clearly indicate that these APKs are rented to affiliates, and Neo_Net possesses the ability to pause or terminate the subscription at any time. Additionally, given his presence in each Telegram chat he establishes, he can monitor every exfiltrated message and potentially profit from compromised victims as well.
Once an account was compromised, the operators employed various methods to withdraw the stolen funds. Some initiated direct transfers to different bank accounts, while others utilized the functionality to withdraw money from ATMs by authorizing cash withdrawals via banking apps. Another method employed involved using online money transfer systems such as Bnext or acquiring digital goods like cryptocurrency or expensive physical items such as watches.

Figure 7: Captured BBVA OTP tokens showing transactions
No new OTP Android trojans have been observed since April 2023, although Neo_Net has announced his intention to resume selling them in the future.
Ankarex – Smishing-as-a-Service
As of July 11th, 2023, Ankarex, Neo_Net’s Smishing-as-a-Service offering, remains operational and continues to undergo active development, with the recent release of version 5.1. This service continually adds new routes in desired countries and enhances existing infrastructure to ensure more reliable SMS delivery. Ankarex has also incorporated payment functionality supporting various cryptocurrencies, simplifying the process for buyers to fund their accounts. When a transaction is requested, a new Bitcoin/Ethereum address is generated, and the funds likely pass through a mixer to obscure tracking of Neo_Net’s main account.
Figure 8: Ankarex recharge Balance page
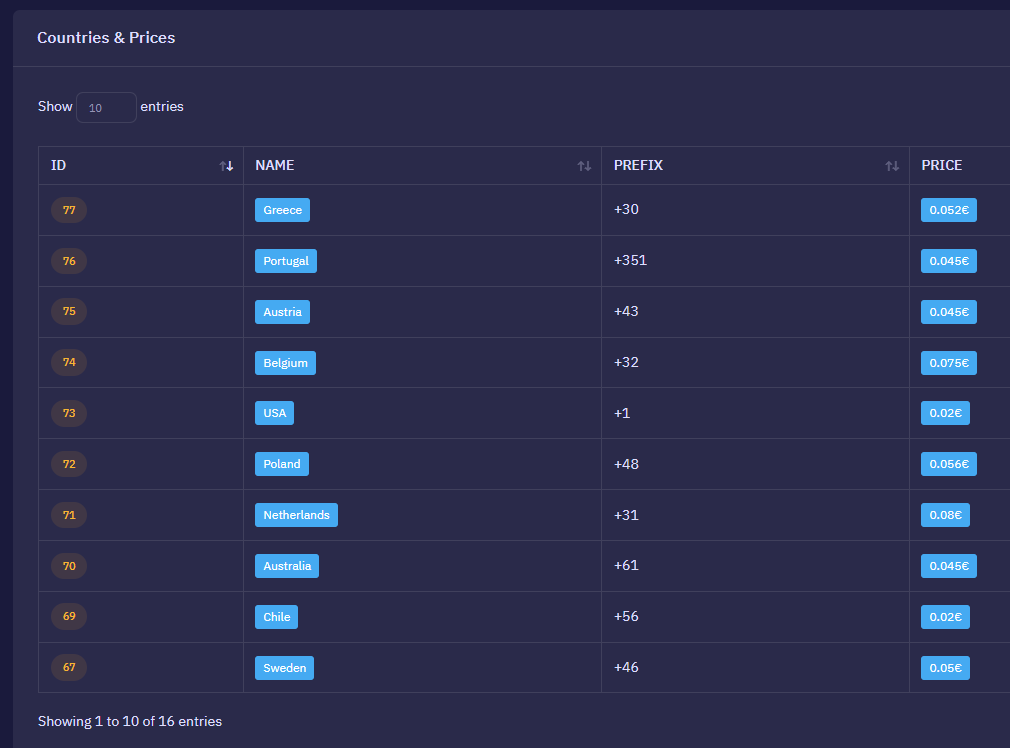
Figure 9: Ankarex targeted countries
Neo_Net promotes his offerings through a Telegram account, which currently boasts over 1,000 subscribers. Regular updates showcase new routes or offer discounts for existing ones. Additionally, Neo_Net has announced plans to introduce further services in the future, including OTP bots, Virtual Private Servers, and antibot solutions for phishing infrastructure.
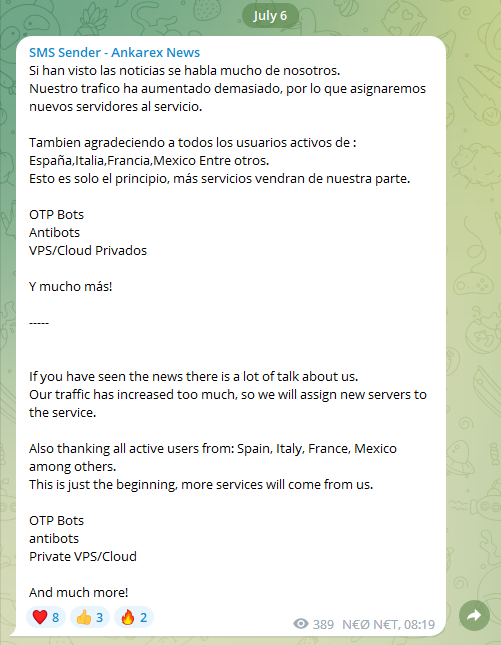
Figure 10: Neo_Net’s announcement on Telegram
Affiliates
Through his extensive range of offerings, Neo_Net has gradually cultivated a network of dozens of affiliates spanning across different regions, primarily Spanish-speaking individuals who target various financial institutions.
These affiliates have been observed collaborating with Neo_Net in various campaigns spanning several months, from October 2022 to April 2023. It is likely that he has cooperated with several other affiliates targeting different institutions but limited visibility into those operations does not allow identifying them.
Conclusion
Neo_Net’s operations over the years demonstrate a remarkable ability to adapt to different scams and campaigns, continuously improving his methods to achieve greater success. The extensive network of affiliates he has established underscores the effectiveness of their setup, as other cybercriminals willingly cooperate with Neo_Net, resulting in substantial financial gains. Neo_Net’s public announcements suggest that he will likely remain a significant threat to Spanish and European citizens, further enhancing his Smishing service and introducing new offerings that contribute to the creation of sophisticated scams. QuoIntelligence will continue to monitor Neo_Net’s activities, tracking his future operations and developments.
MITRE ATT&CK Tags
| ID | Technique | Explanation |
| T1583.008 | Acquire Infrastructure: Malvertising | Neo_Net purchased Google Ads to trick victims into visiting his fake crypto wallet websites |
| T1566.002 | Phishing: Spearphishing Link | Neo_Net sends phishing links over SMS to his victims |
| T1437.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | The Android OTP bot exfiltrates SMS messages over HTTPS |
| T1481.003 | Web Service: One-Way Communication | The OTP bot and the phishing panels use Telegram to forward data to the operators in a chat |
| T1521.002 | Encrypted Channel: Asymmetric Cryptography | The C2 channel is encrypted using TLS |
If you wish to keep up-to-date with the latest developments on the threat landscape and other cyber and geopolitical threats, request a free subscription to our Weekly Intelligence Snapshot issued every Thursday at 1900CET.





